From: https://vpha.org.vn/covid-19/dich-te-hoc-covid-19-trong-qua-khu.html
1. Timeline
Late 2019 – Early 2020
In December 2019, Wuhan, China, was the initial source of the COVID-19 pandemic. 2 Both the fish and animal markets here were closed when cases of pneumonia appeared. On 9 January 2020, WHO confirmed that a new coronavirus was isolated from a hospitalized person. On January 11, the first death from the virus occurred. During January, cases appeared in various locations, including Thailand and European countries. 3 Faced with this situation, countries have imposed containment measures, such as closing borders and restricting travel from China. On January 30, WHO declared it an international public health emergency. On March 11, WHO declared the COVID-19 acute respiratory infection caused by a new strain of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) a global pandemic. 4
From the end of 2020 until now
From the end of 2020 until now, many countries around the world have approved and launched vaccination campaigns with many different vaccines to control the COVID-19 pandemic. In December 2020, the US Federal Government approved and launched the vaccination campaign with the first vaccine developed by Pfizer-BioNTech . Just a few days later, on December 14, Canada also began a vaccination campaign using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. Next, on December 27 of the same year, the European Union began a vaccination campaign with the same vaccine. In addition, it is not limited to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, but there is also the approval and deployment of many other vaccines such as Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Sinovac. 5 Countries around the world are actively developing and implementing mass vaccination strategies, leading to significant reductions in infections and deaths.
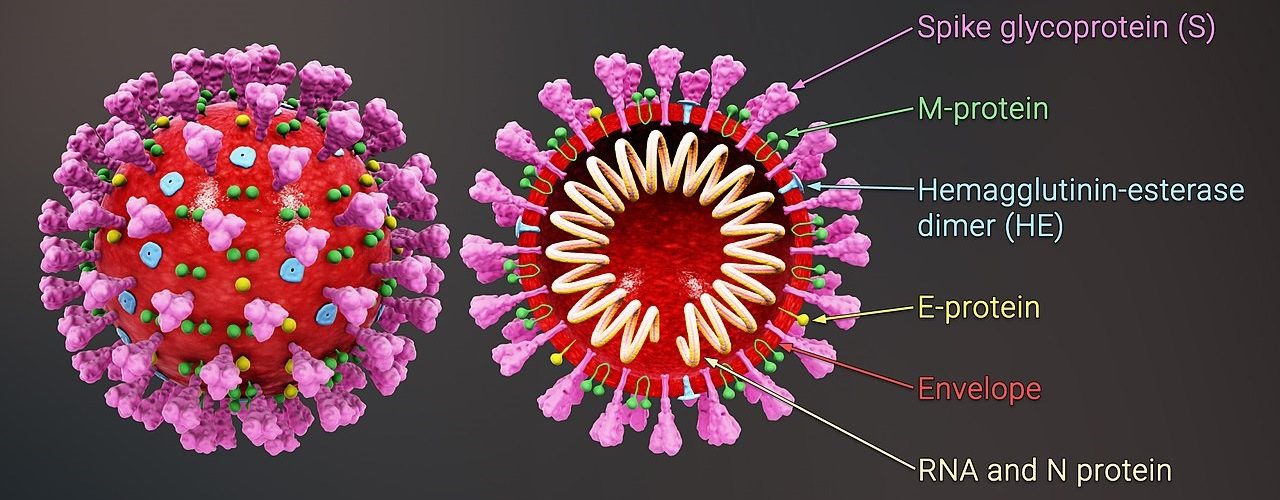
2. Origin of Sar-CoV-2 virus
Originating in late December 2019 with the first epidemic center in Wuhan city in central mainland China, originating from a group of people with pneumonia of unknown cause. Local health officials confirmed that they had previously been in contact, mainly with traders trading and working at the Hoa Nam seafood market. 2
3. How it is transmitted
The disease is determined to be transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets when a person with the disease sneezes, coughs or exhales. The disease also spreads indirectly when healthy people’s hands come into contact with objects contaminated with the virus such as condoms, sanitary napkins… especially objects contaminated with nasopharyngeal fluid from people with COVID-19 after that puts their hands in their eyes, nose, or mouth and causes infection. 6
4. Incubation period
An infected person may develop symptoms after an incubation period of 2 to 14 days , with an average of 5-6 days, during which time it remains contagious. 7
5. Symptoms:
Reported symptoms depend on the type of virus, but common signs include respiratory symptoms, fever, cough and difficulty breathing. In more severe cases, the infection can cause pneumonia, severe acute respiratory syndrome, kidney failure and even death. 8
However, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 25% of patients may have no symptoms or unclear symptoms. 9
6. High Risk Group : 7
People 60 years of age or older and people with underlying medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, other chronic health problems (e.g., those affecting the heart, lungs, kidneys, and brain) , low immune function/immunosuppression (including HIV), obesity, cancer, and unvaccinated people are at highest risk for severe illness.
However, anyone of any age can get COVID-19 and become seriously ill or die.
7. Global Spread:
January 2020: The World Health Organization (WHO) announced that Chinese health authorities had identified the cause of the pneumonia outbreak as a new type of corona virus, D614G. 10 The virus subsequently spread to other provinces of mainland China and other countries, including Thailand, Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, Australia, France, the United States, and Vietnam. 11 , 12
As of March 11, 2020: worldwide there have been 118,319 confirmed cases of infection, 4,292 deaths. Cases outside China have been present in 113 countries and territories around the world. In that context, WHO declared the COVID-19 acute respiratory infection epidemic caused by the new strain of Corona virus (SARS-CoV-2) to be a global pandemic. 13 Early April 2020: The number of COVID-19 cases globally exceeded 1 million. WHO reports evidence that people infected with SARS-CoV-2 can transmit the virus to others even before showing signs of illness. 14
8. Virus Variations :
From September to December 2020, new variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus appeared in the UK, South Africa, Brazil, and India. WHO classifies them as Variants of Concern (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta) due to their ability to spread faster and affect the effectiveness of control measures. 15 , 16 The Delta variant has sparked a wave of epidemics with global COVID-19 deaths exceeding the 4 million mark. Delta became the dominant variant worldwide. 17
November 2021: A new SARS-CoV-2 variant was discovered in southern Africa, immediately classified as a Variant of Concern and named Omicron. In 2022, sub-lines arising from Omicron will continuously appear, causing new waves of infections such as BA.4, BA.5, BA.2.75,… 18
References:
- Scientific Annimations. Coronavirus Symptoms and Prevention Explained Through Medical Animation. https://www.scientificanimations.com/coronavirus-symptoms-and-prevention-explained-through-medical-animation/
- Cục Y tế Dự phòng. Tình hình và các biện pháp phòng, chống dịch bệnh viêm phổi cấp do chủng coronavirus mới tại thành phố Vũ Hán, tỉnh Hồ Bắc, Trung Quốc. https://vncdc.gov.vn/tinh-hinh-va-cac-bien-phap-phong-chong-dich-benh-viem-phoi-cap-do-chung-coronavirus-moi-tai-thanh-pho-vu-han-tinh-ho-bac-trung-quoc-nd15004.html
- WHO. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCov): Situation Report – 5. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200125-sitrep-5-2019-ncov.pdf?sfvrsn=429b143d_8
- Bộ Y tế. WHO tuyên bố COVID-19 là đại dịch toàn cầu. https://moh.gov.vn/chuong-trinh-muc-tieu-quoc-gia/-/asset_publisher/7ng11fEWgASC/content/who-tuyen-bo-covid-19-la-ai-dich-toan-cau
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overview of COVID-19 Vaccines. Overview of COVID-19 Vaccines | CDC
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Covid-19. https://web.archive.org/web/20210324224953/https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/how-covid-spreads.html
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-answers-hub/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19
- WHO. Q$A on coronaviruses. https://web.archive.org/web/20200120174649/https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses
- Đài truyền hình Việt Nam. 25% ca mắc COVID-19 không triệu chứng. https://vtv.vn/suc-khoe/25-ca-mac-covid-19-khong-trieu-chung-20200403021531109.htm
- Bộ Y tế. SARS-COV-2 đột biến tạo biến thể ra sao? https://covid19.gov.vn/sars-cov-2-dot-bien-tao-bien-the-ra-sao-1717355235.htm
- Cục Y tế Dự phòng. Hai trường hợp bước đầu được xác định nhiễm chủng vi rút Corona mới nCoV tại Việt Nam (Ngày 24 tháng 01 năm 2020). https://vncdc.gov.vn/hai-truong-hop-buoc-dau-duoc-xac-dinh-nhiem-chung-vi-rut-corona-moi-ncov-tai-viet-nam-ngay-24-thang-01-nam-2020-nd15025.html
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Novel coronavirus: three cases reported in France. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/novel-coronavirus-three-cases-reported-france
- WHO. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report – 51. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200311-sitrep-51-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=1ba62e57_10
- WHO. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report – 75. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200404-sitrep-75-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=99251b2b_4
- Bệnh viện Đa khoa Tâm Anh. 5 BIẾN THỂ COVID 19 PHỔ BIẾN: BIẾN CHỦNG NÀO NGUY HIỂM NHẤT? https://tamanhhospital.vn/bien-the-covid-19/
- National Department Of Health. Update on Covid-19 (18th December 2020). https://sacoronavirus.co.za/2020/12/18/update-on-covid-19-18th-december-2020/
- Đài truyền hình Việt Nam. Số ca tử vong do COVID-19 tăng mạnh ở Campuchia và Thái Lan, biến thể Delta lây lan nghiêm trọng trên thế giới. https://vtv.vn/the-gioi/so-ca-tu-vong-do-covid-19-tang-manh-o-campuchia-va-thai-lan-bien-the-delta-lay-lan-nghiem-trong-tren-the-gioi-20210703162209007.htm
- WHO. Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.1.529)-sars-cov-2-variant-of-concern



















Add comment